Types of Gum Grafting Surgeries
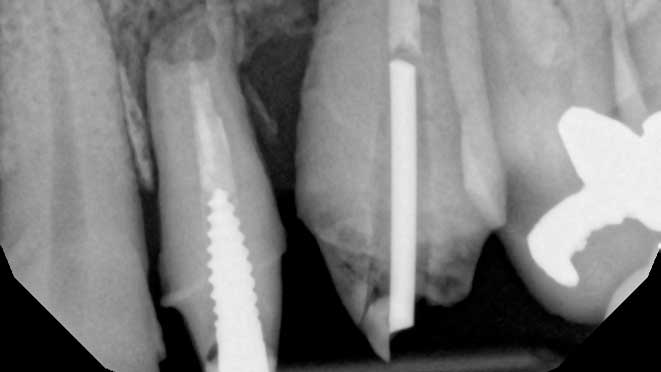
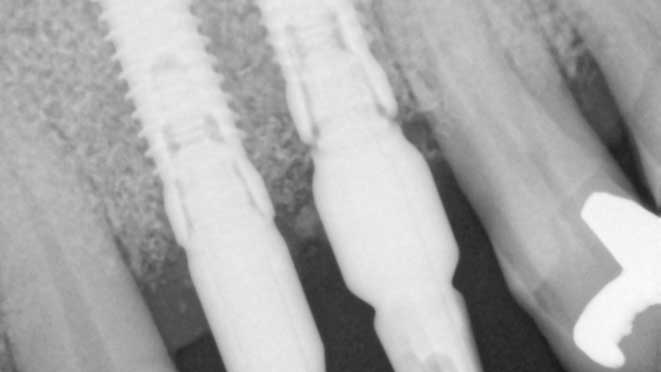
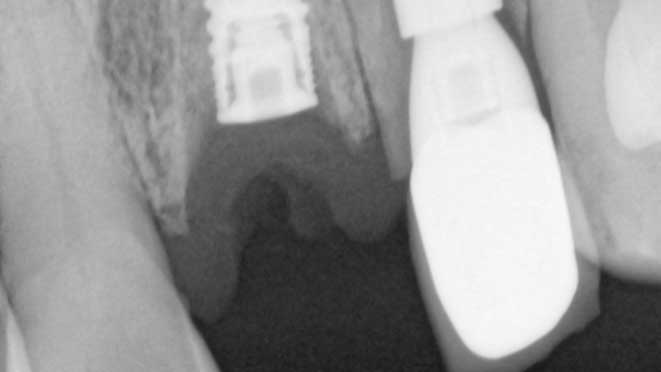
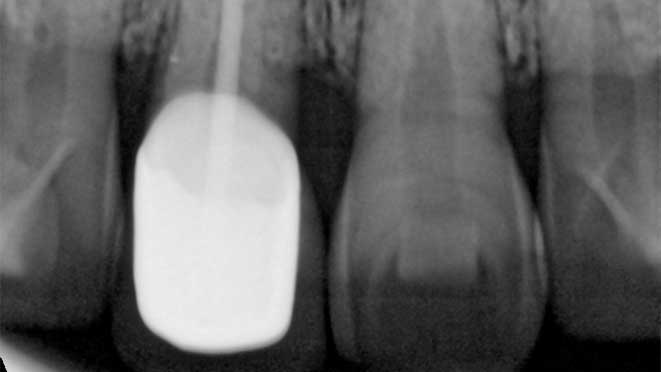
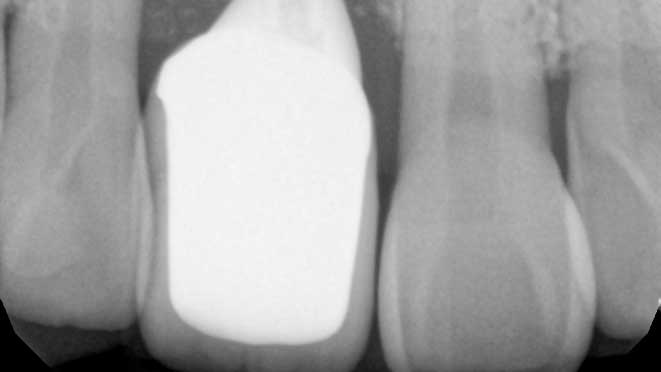
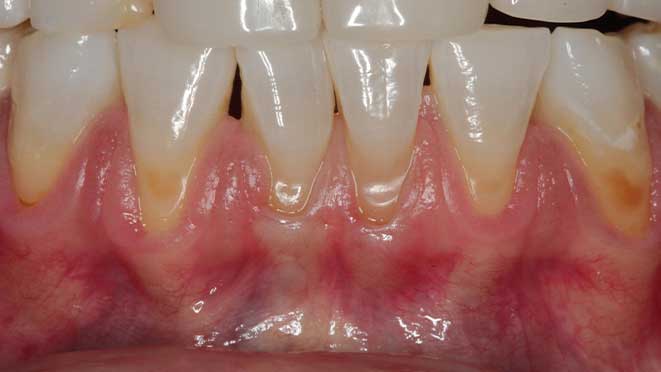
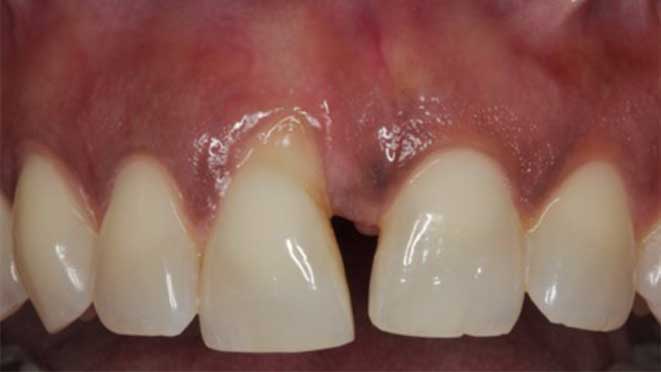
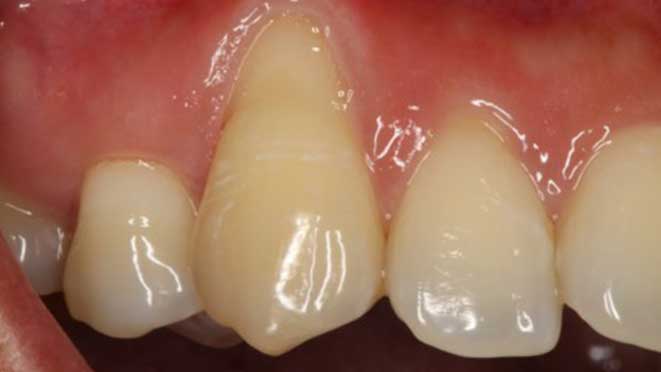
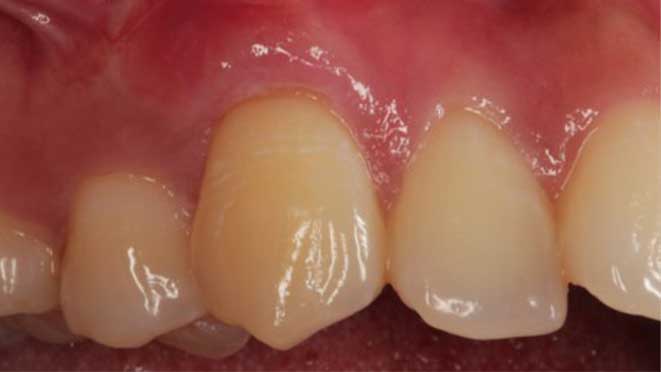
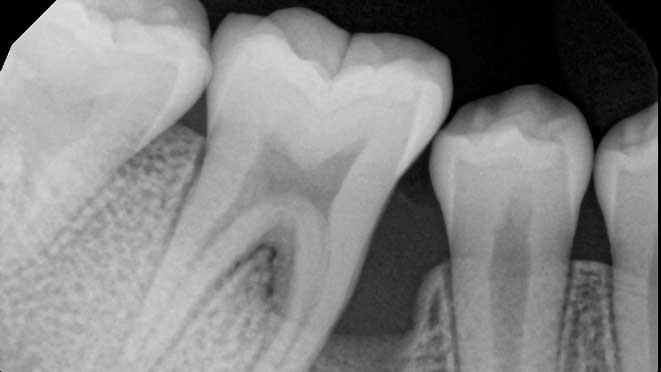
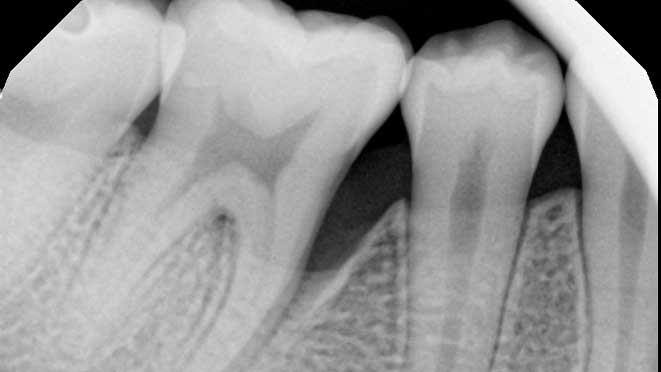
Gum grafting surgeries fall into three categories: connective-tissue grafts, free gingival grafts, and pedicle grafts. The first type, connective-tissue grafts, involves taking a small piece of tissue from the roof of the mouth and stitching it onto the affected gum area. Free gingival grafts, on the other hand, involve taking gum tissue directly from the roof of the mouth and attaching it to the receded gum line. Lastly, pedicle grafts involve using gum tissue from nearby teeth and stretching it over the exposed root.
Connective-tissue grafts are usually recommended for patients with moderate to severe gum recession. The surgery is performed under local anesthesia, and patients can resume normal activities within a few days. Free gingival grafts, on the other hand, are best suited for patients with thin gums who require more tissue. Pedicle grafts may also be recommended for patients with multiple receded areas, and the surgery involves less trauma to oral tissues.
Benefits of Gum Grafting
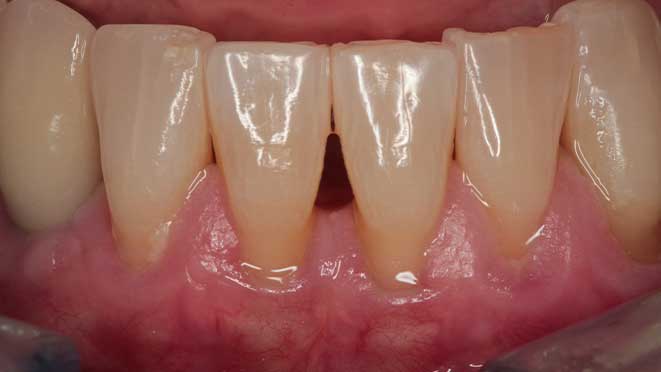
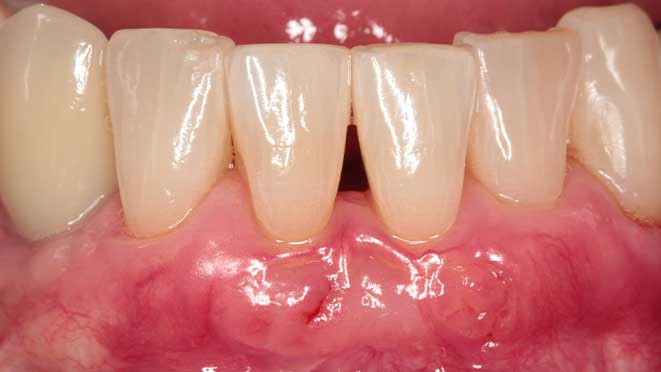
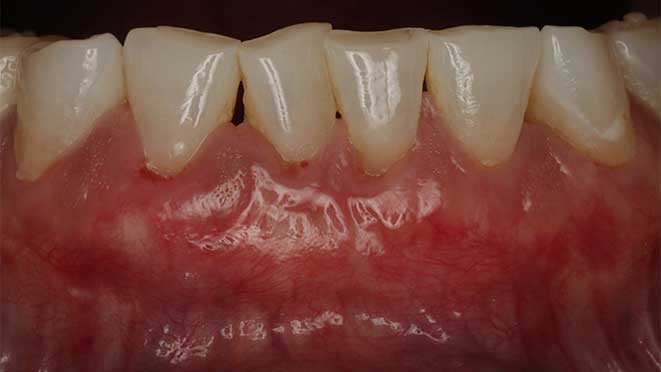
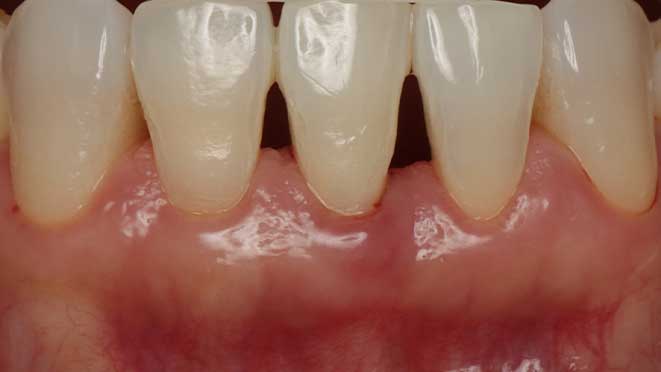
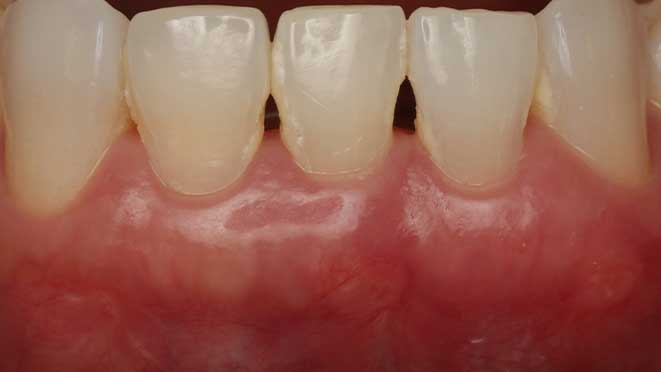
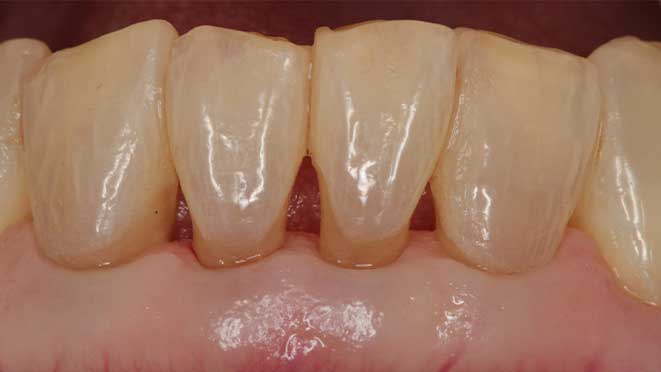
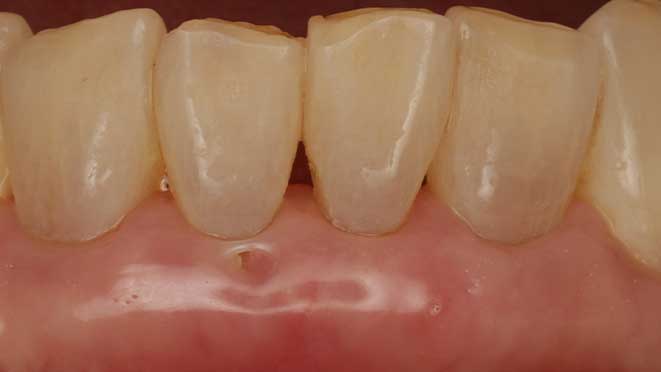
Gum grafting offers numerous benefits, one of which is improved gum health. The procedure helps to prevent gum disease by eliminating pockets around teeth that can trap bacteria, leading to inflammation and infection. Additionally, gum grafting improves the appearance of teeth, especially for patients with receding gums, creating a more symmetrical and attractive smile. Lastly, the surgery can significantly reduce tooth sensitivity, making eating and drinking more comfortable.
Post-Operative Care
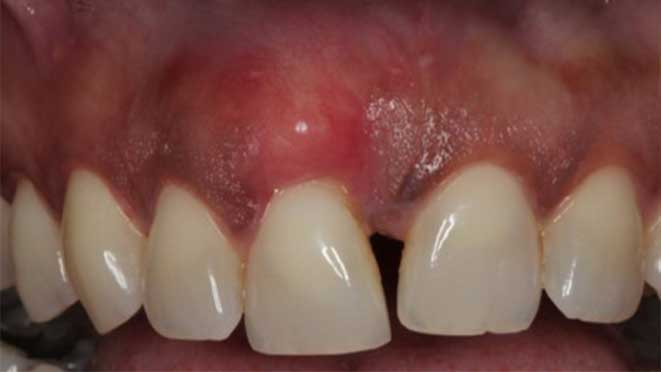
Like every surgery, post-operative care is essential for a successful recovery. After gum grafting surgery, patients should expect some swelling and discomfort for about a week. Pain medication may be prescribed to manage discomfort, and patients should rest as much as possible during the healing process. During the first day after surgery, patients should avoid brushing and flossing in the affected area. A soft diet should be followed for a few days to minimize the chance of damaging the healing site. As healing progresses, patients can gradually resume their normal oral hygiene routine while being careful around the treated area.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bone grafting is an excellent option for those experiencing bone loss due to missing teeth. The process involves removing damaged or infected bones and replacing them with grafting materials like autogenous, allografts, or xenografts. The advantages of bone grafting are numerous, and it offers an opportunity to attain better jawbone density, oral health, and be aesthetically pleasing. Finally, bone grafting remains an intricate surgical process that requires post-operative care, nutrition, and lifestyle changes to ensure the optimal outcome. It is always best to consult your dentist or oral surgeon to determine if bone grafting is right for you, so make sure to schedule an appointment.